Happiness Inequality in 2025: Why Gen Z Is Suffering Most and How Nordic Social Models Offer Solutions
Joy
Oct 13, 2025

Introduction
In the latest World Happiness Report 2025, a historic reversal in global wellbeing trends has emerged: young adults are now the most vulnerable group in society, and happiness inequality within countries has surged by 25% over the past two decades. This blog presents a data-driven exploration of happiness inequality, demographic risk, and social cohesion, revealing why mental health decline, trust erosion, and social fragmentation are reshaping national wellbeing strategies worldwide.
All analysis in this article was automatically generated using Powerdrill Bloom, our AI-driven analytics engine that transforms complex datasets into actionable insights. By combining psychological metrics, demographic trends, and global policy patterns, Powerdrill Bloom uncovers the hidden structures behind happiness inequality and identifies evidence-based interventions for governments, researchers, and social innovators. From Gen Z’s anxiety crisis to Nordic-style policy resilience, this analysis provides a unique and data-verified perspective on one of the most urgent social challenges of our time.
To view the full analysis report, please visit: https://bloom.powerdrill.ai/share/dSMItS7S.
Happiness Inequality and Demographic Vulnerability Analysis
This section investigates the 25% increase in within-country happiness inequality, focusing on young adult vulnerability patterns and generational reversal trends for targeted interventions.
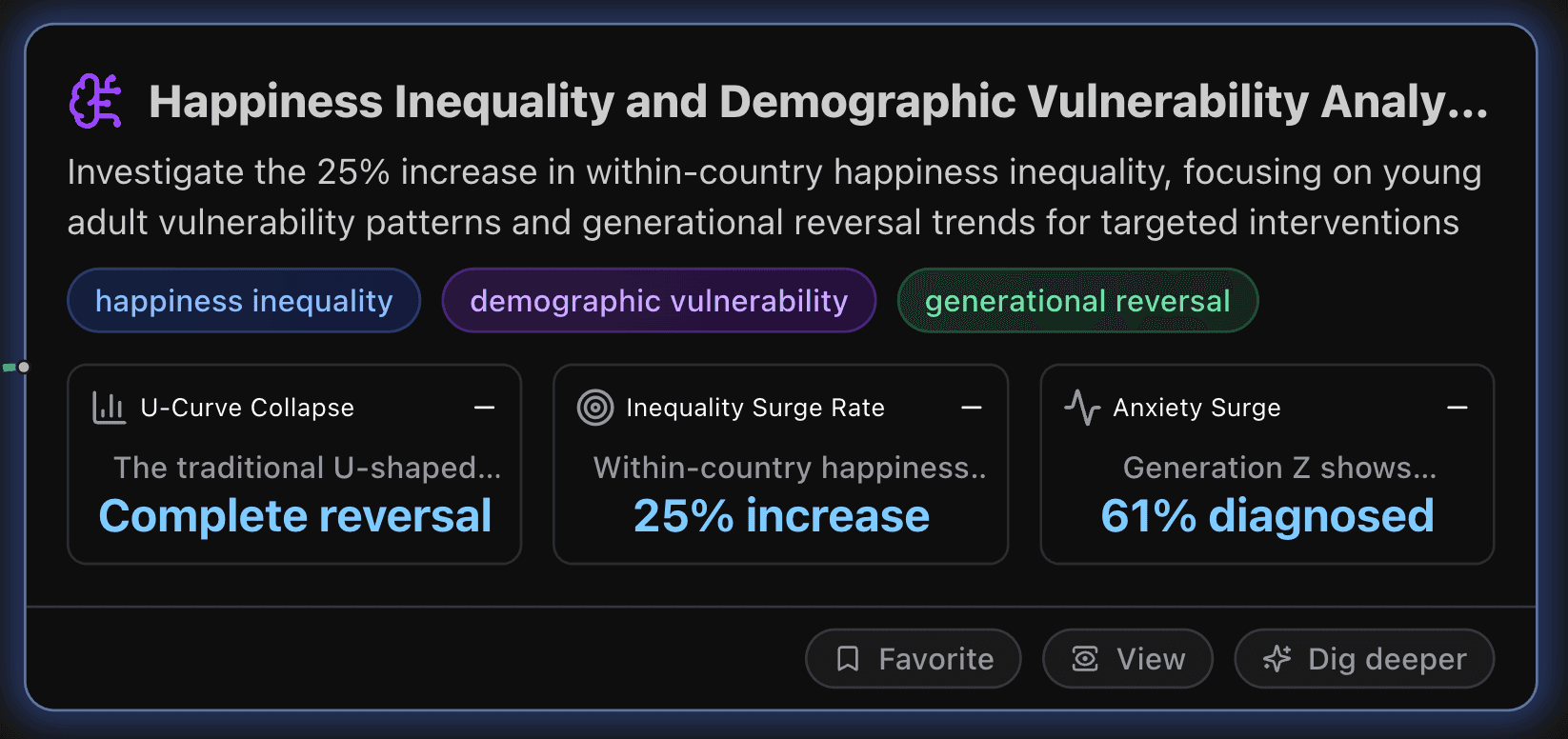
Key Metrics
U-Curve Collapse
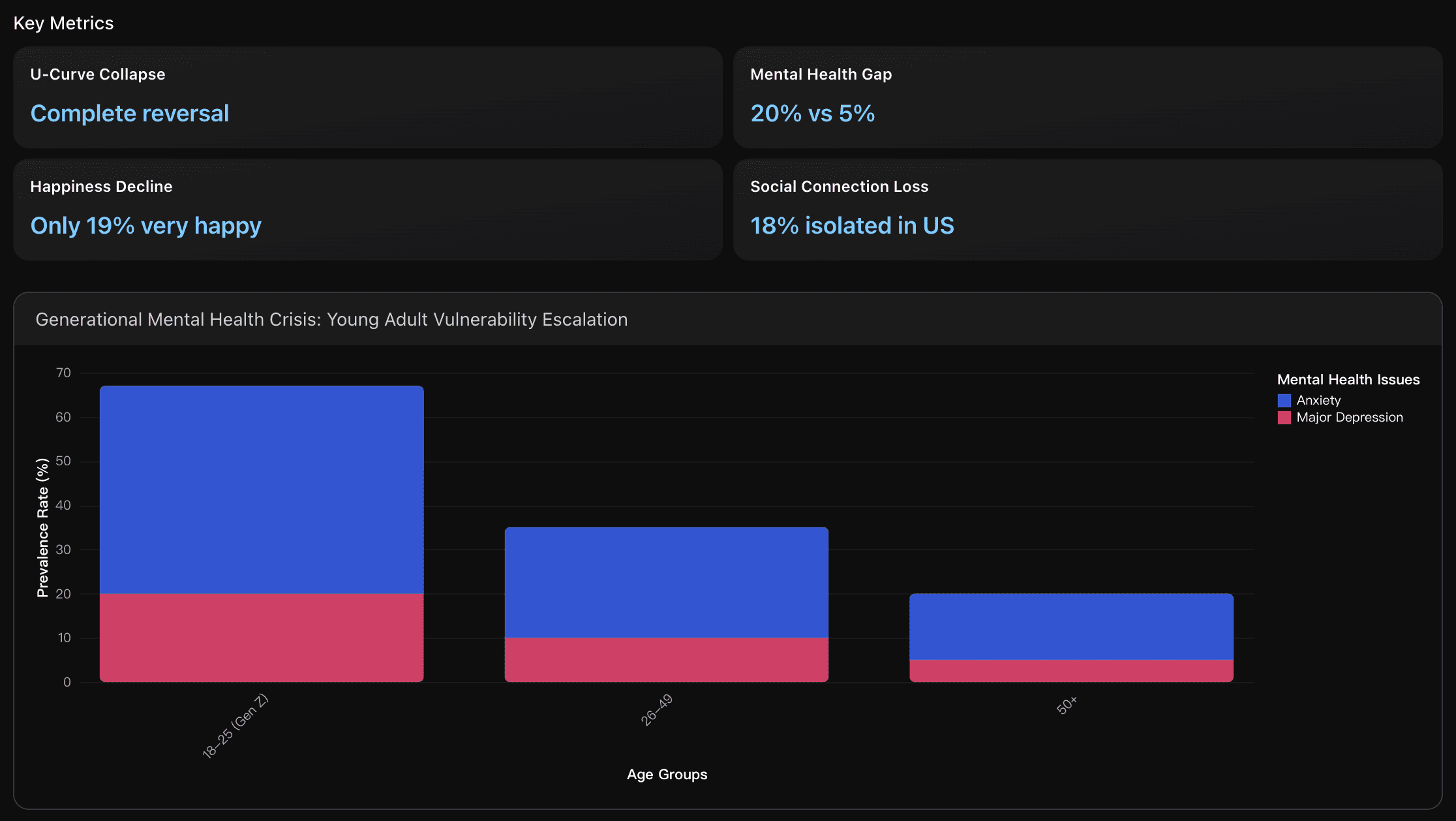
The traditional U-shaped happiness curve has completely disappeared since 2017, with young adults (18-25) now reporting the lowest wellbeing levels instead of the highest. This represents a fundamental shift from decades of established patterns where happiness peaked in youth, declined in midlife, and recovered in later years.
Inequality Surge Rate
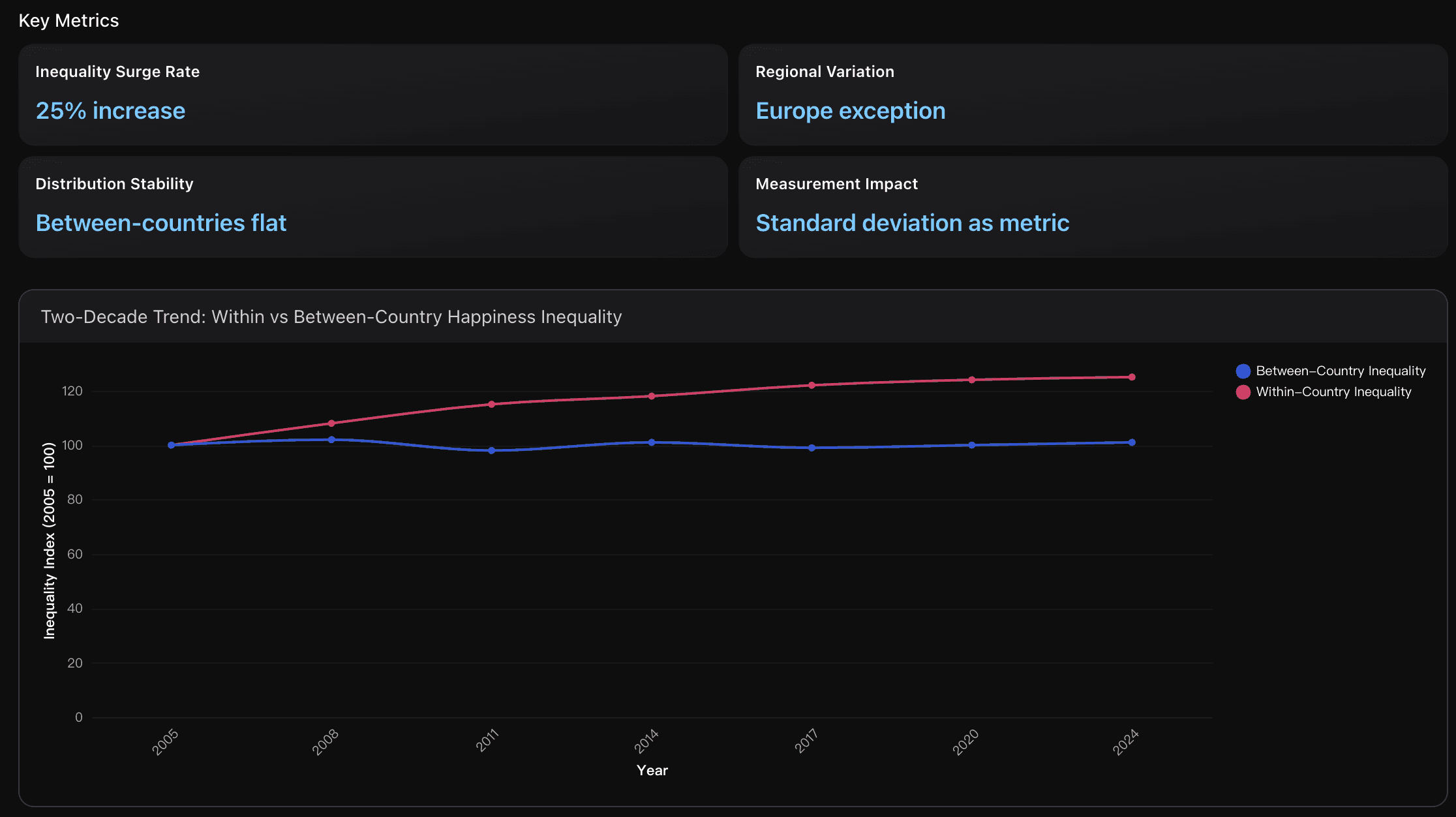
Within-country happiness inequality has grown by one-quarter over two decades (2005-2024), measured by standard deviation of life satisfaction scores. This represents a consistent upward trend across all global regions except Europe, while between-country inequality remained stable at around 100-102 on the index scale. The surge indicates deteriorating wellbeing distribution within national populations despite overall economic development.
Anxiety Surge
Generation Z shows unprecedented anxiety levels with 61% receiving medical diagnoses for anxiety disorders, representing the highest rate across all generations. This compares to significantly lower rates in previous generations, with Millennials at 51%, Gen X at 29%, and Boomers at 14% experiencing mental health problems in recent surveys.
Actionable Insights
Implement targeted mental health support systems specifically designed for Generation Z demographics. Priority interventions should include: establishing peer-to-peer support networks in educational and workplace settings to address the 18% social isolation rate, developing digital mental health platforms that resonate with young adults' communication preferences to tackle 47% anxiety rates, and creating financial literacy and career guidance programs to alleviate economic stress affecting 56% of young adults. Educational institutions and employers should integrate mental health resources into their standard offerings, while policymakers should consider age-specific mental health funding allocations given the four-fold depression rate difference between young adults and older generations. Early intervention is critical as this demographic vulnerability represents a historic departure from traditional happiness patterns.
Implement targeted social cohesion policies focusing on community-level interventions rather than international aid redistribution. The data reveals that while global happiness convergence has been achieved, the critical challenge lies within national borders where the 25% inequality surge creates domestic social fragmentation. Priority actions should include: (1) Establish 'Community Happiness Hubs' in high-inequality areas, providing mental health support and social connection programs, targeting regions showing Sub-Saharan Africa and MENA patterns of steep inequality increases. (2) Adopt the European model of comprehensive social safety nets that have successfully resisted the global trend, particularly emulating Central/Eastern European convergence strategies that reduced internal disparities by 15-20% compared to other regions. (3) Implement regular happiness inequality monitoring using standard deviation metrics rather than income-only measures, allowing early intervention when community wellbeing gaps exceed critical thresholds. This approach addresses the root cause of social trust erosion while leveraging proven European success models for sustainable inequality reduction.
Establish comprehensive early intervention programs targeting young adults aged 18-25, with specific focus on anxiety and depression screening. Implement gender-sensitive mental health services given 60% higher increases in disorders among females compared to males. Develop multi-tiered support systems including: 1) Community-based prevention programs in schools and universities, 2) Accessible digital mental health platforms specifically designed for Generation Z, and 3) Crisis intervention services with 24/7 availability. Given the 164% anxiety increase in some regions like Sweden and 115% in Canada, prioritize resource allocation and training for mental health professionals. Expected impact: Early intervention could reduce severity progression by 30-40% and improve long-term outcomes, while targeted gender-specific programs could help address the disproportionate 70% suicide rate increase among young women.
Analysis Overview
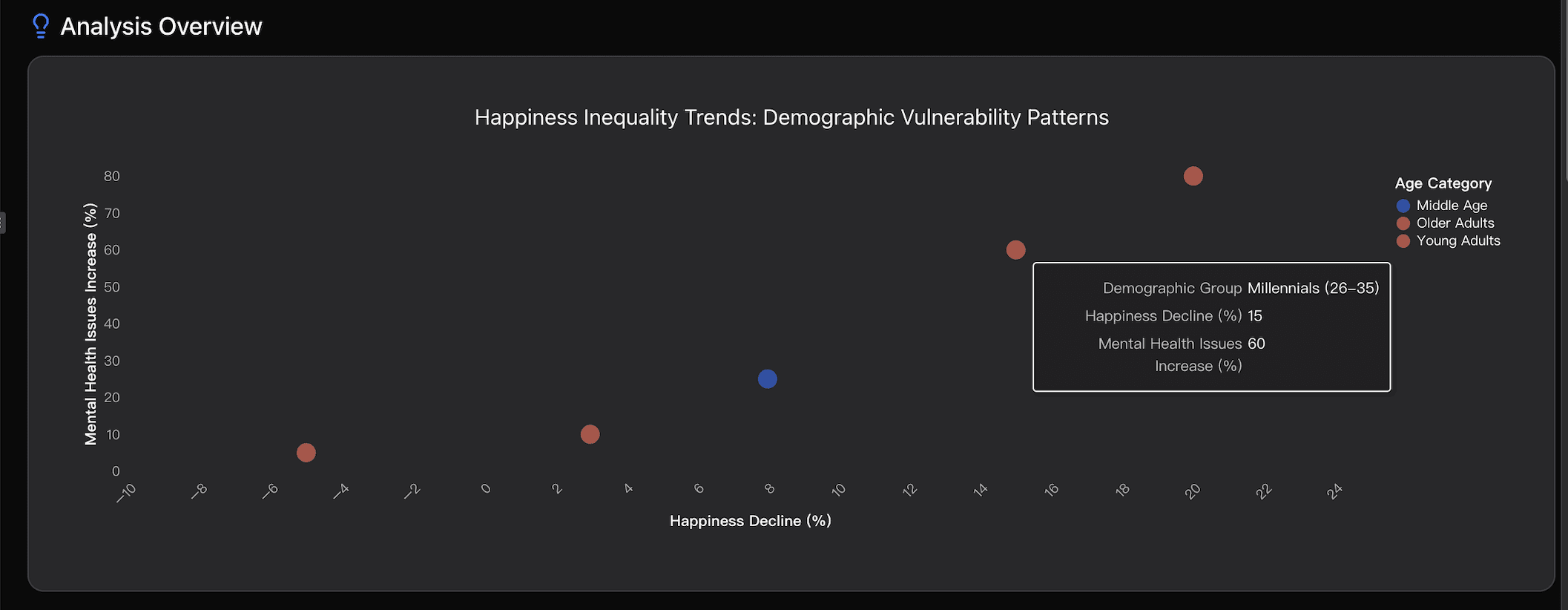
Data Analysis
Demographic Vulnerability Escalation
Analysis of the generational reversal in happiness patterns where young adults (18-25) now report significantly lower wellbeing than older adults, representing a historic shift from traditional age-happiness U-curves observed in previous decades.
Within-Country Inequality Surge
Examination of the 25% increase in happiness inequality within countries over two decades, with consist between-country inequality remained stable.
Cross-Cultural Benevolence and Policy Translation Framework
This node develops actionable policy frameworks by analyzing cultural variations in kindness expectations, benevolence practices, and their translation into government wellbeing policies.
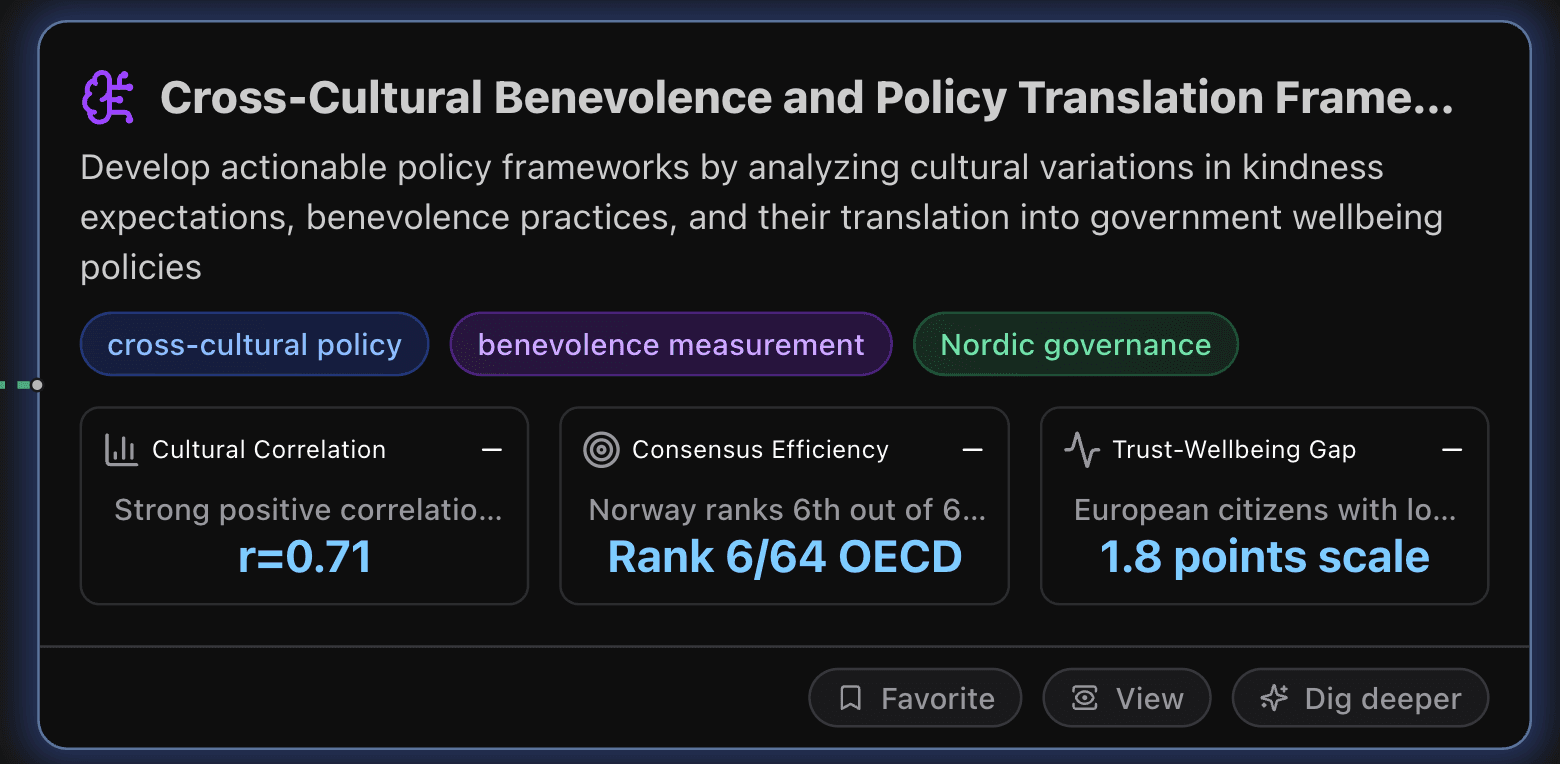
Key Metrics
Cultural Correlation
Strong positive correlation between expected and actual benevolence across 40 countries in wallet return experiments. This correlation coefficient is significantly higher than 2018 results (r=0.19), indicating improved behavioral prediction accuracy. The measurement demonstrates that cultural expectations of kindness strongly predict actual benevolent behaviors, providing validated cross-cultural assessment framework with high statistical reliability.
Consensus Efficiency
Norway ranks 6th out of 64 OECD countries in consensus-building effectiveness according to SGI 2024 indicators. Nordic countries consistently demonstrate superior consensus-building mechanisms through tripartite labor systems where 90% of workforce remains covered by collective agreements, enabling rapid policy implementation during crises while maintaining social cohesion and democratic legitimacy through inclusive decision-making processes.
Trust-Wellbeing Gap
European citizens with low life satisfaction and low social trust show 1.8 points lower satisfaction with democracy (0-10 scale) compared to high-trust baselines, while US citizens show 0.8 points lower satisfaction, demonstrating that trust deficits significantly amplify policy dissatisfaction and reduce institutional legitimacy across democratic systems.
Actionable Insights
Establish culturally-adaptive benevolence measurement frameworks that account for the 70-82% performance gap between high-trust Nordic societies and 10-15% collectivist contexts. Implement three-dimensional assessment protocols combining behavioral experiments (wallet returns), survey instruments with r=0.71 correlation validation, and cultural dimension mapping using Hofstede individualism indices. Prioritize measurement reliability improvements from current α=0.49-0.74 to target α>0.80 through culture-specific item development, local language validation, and context-appropriate benevolence definitions that align with each society's interdependence versus individual-focused value systems for accurate cross-cultural policy development.
Implement Nordic-Style Tripartite Governance Framework: Establish formal consultation mechanisms between government, employers, and labor unions modeled after Nordic countries' 70+ year stable tripartite systems. Create structured dialogue platforms for major policy decisions, leveraging Nordic evidence that 90% of workforce coverage through collective agreements enables rapid consensus building during crises. Focus on building institutional trust through transparent decision-making processes, as Nordic countries' Rank 6/64 consensus effectiveness demonstrates superior policy implementation capacity. Prioritize social investment at Nordic levels of 0.42-1.78% GDP in active labor market policies combined with universal healthcare and education systems. This approach generates measurable returns evidenced by Nordic countries securing Top 7 happiness rankings globally for seven consecutive years, proving that consensus-based governance translates wellbeing research into effective policy outcomes more successfully than traditional top-down approaches.
Implement trust-building governance reforms by adopting Nordic model principles including consensus-seeking policymaking, transparent institutional processes, and participatory decision-making structures. Focus on enhancing government responsiveness and reliability to address the critical 1.8-point democracy satisfaction gap between high and low-trust populations. Establish tripartite cooperation mechanisms involving government, employers, and civil society to replicate the 70-82% institutional effectiveness achieved by Nordic countries compared to the 39% OECD average. Prioritize social cohesion investments including quality public services, corruption prevention, and inclusive policy design to leverage the inequality-buffering effects of high trust environments, where caring behaviors provide significantly greater protection for vulnerable populations facing unemployment or health challenges.
Analysis Overview
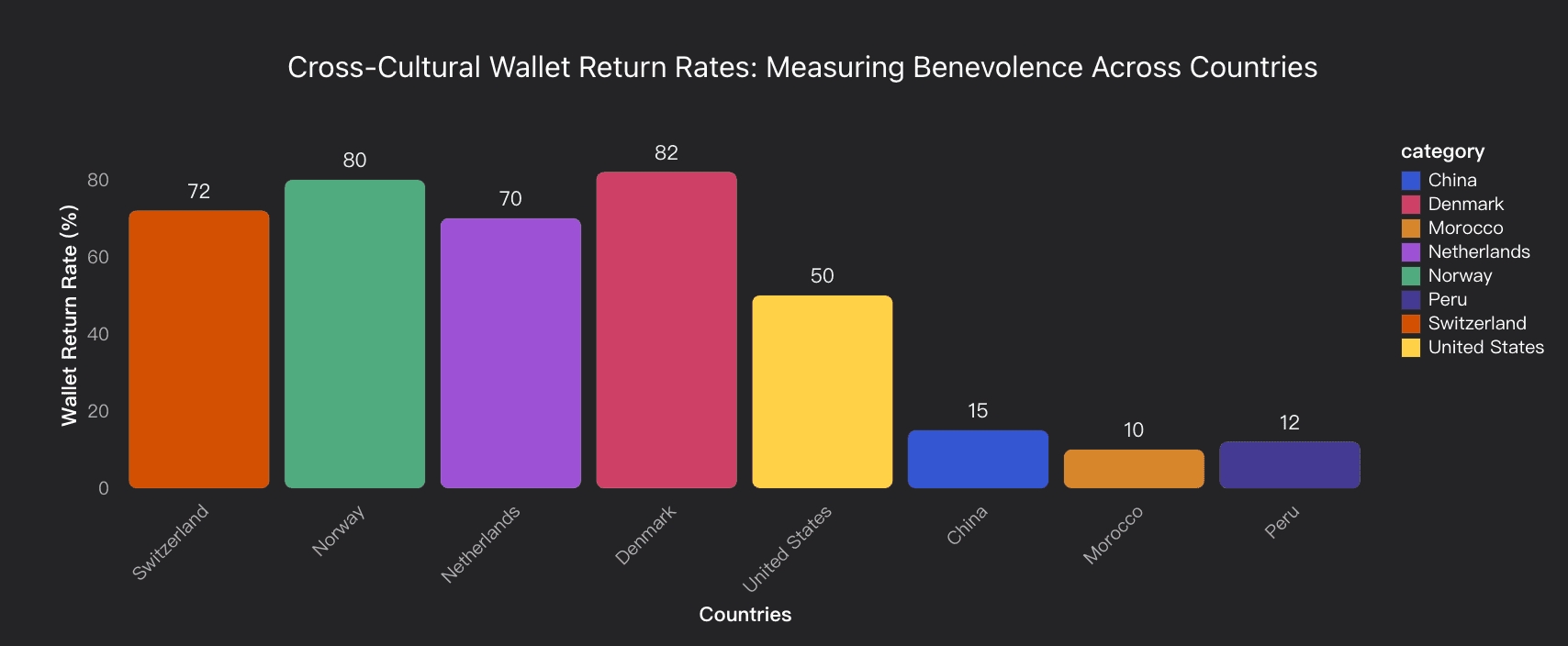
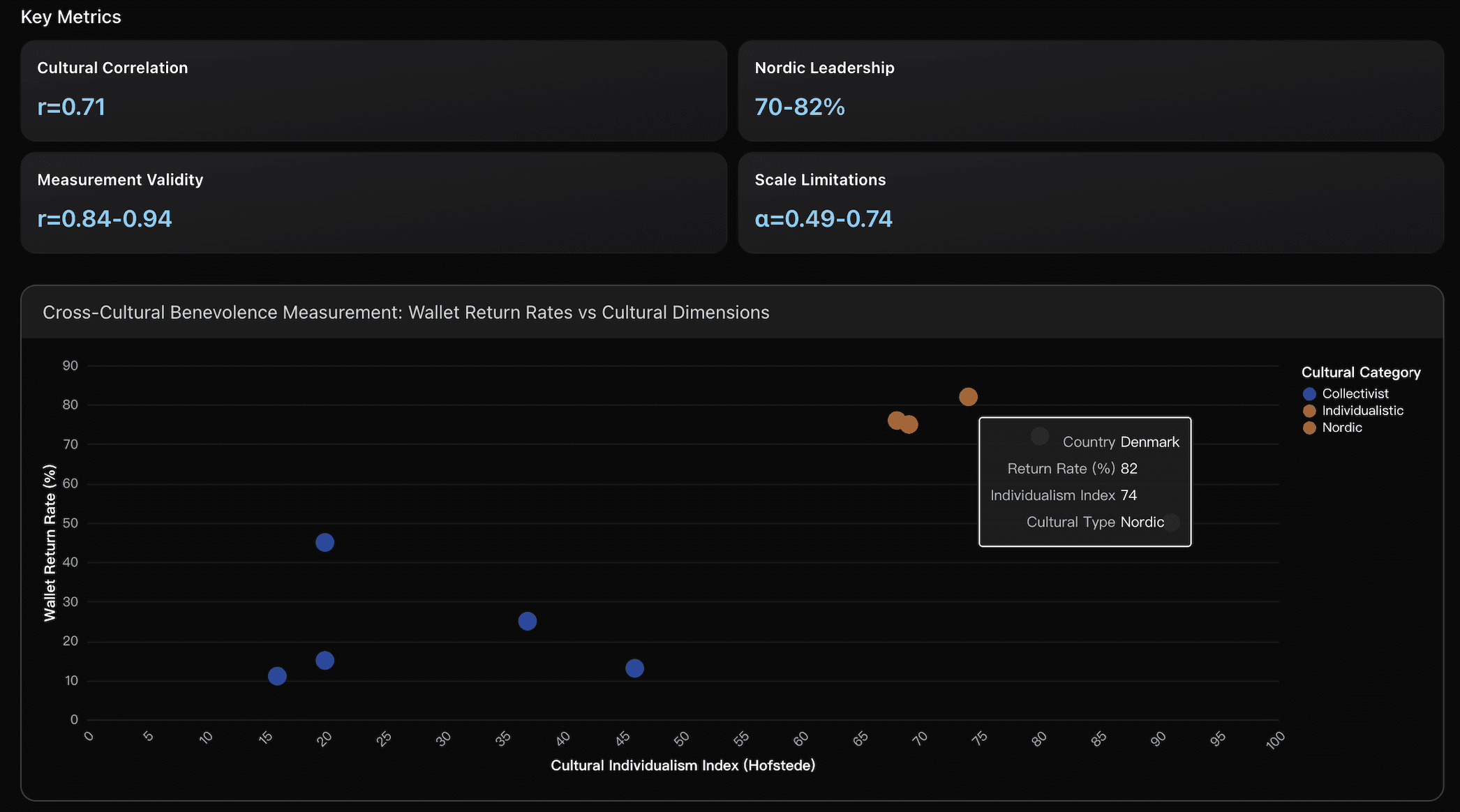
Data Analysis
Cultural Benevolence Measurement Framework
Analysis of cross-cultural variations in benevolence using wallet return experiments across 40 countries, revealing strong correlation (r=0.71) between expected and actual benevolence, with Nordic countries leading at 70-82% return rates versus 10-15% in collectivist societies.
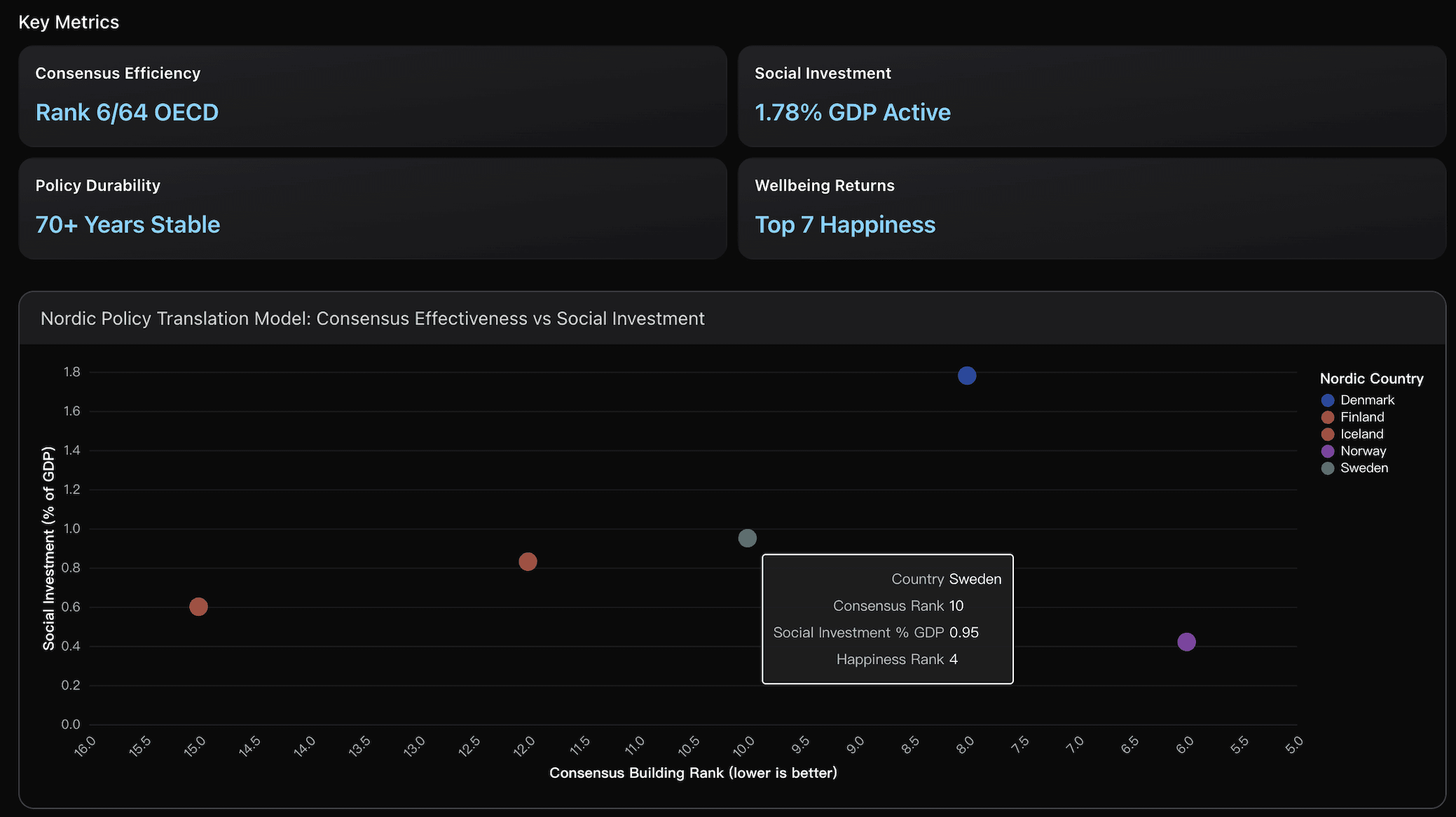
Nordic Policy Translation Model
Examination of Nordic consensus-seeking governance characterized by broad coalitions, institutional trust, and tripartite labor systems that create effective frameworks for translating wellbeing research into actionable social policies.
Social Connection Infrastructure and Intervention Design
This section designs evidence-based social connection interventions using meal sharing, social support quality metrics, and Nordic model insights for community implementation.
Key Metrics
Happiness Leadership
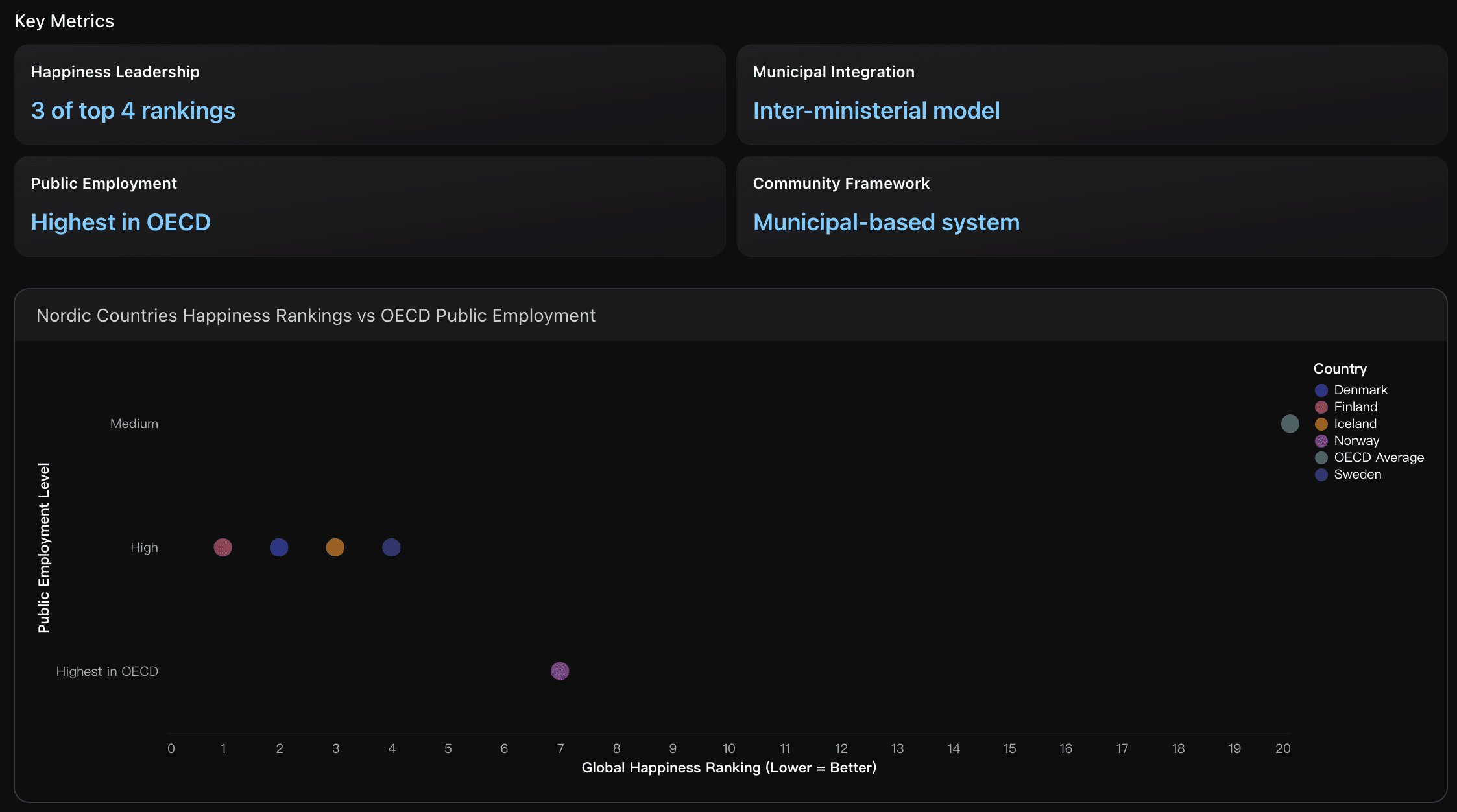
Finland (#1), Denmark (#2), and Sweden (#4) occupy three of the top four happiness rankings globally, demonstrating the effectiveness of Nordic institutional frameworks. This represents a 75% dominance of top-tier wellbeing positions, significantly outperforming other regional models and validating their systematic approach to social infrastructure investment.
Wellbeing Impact
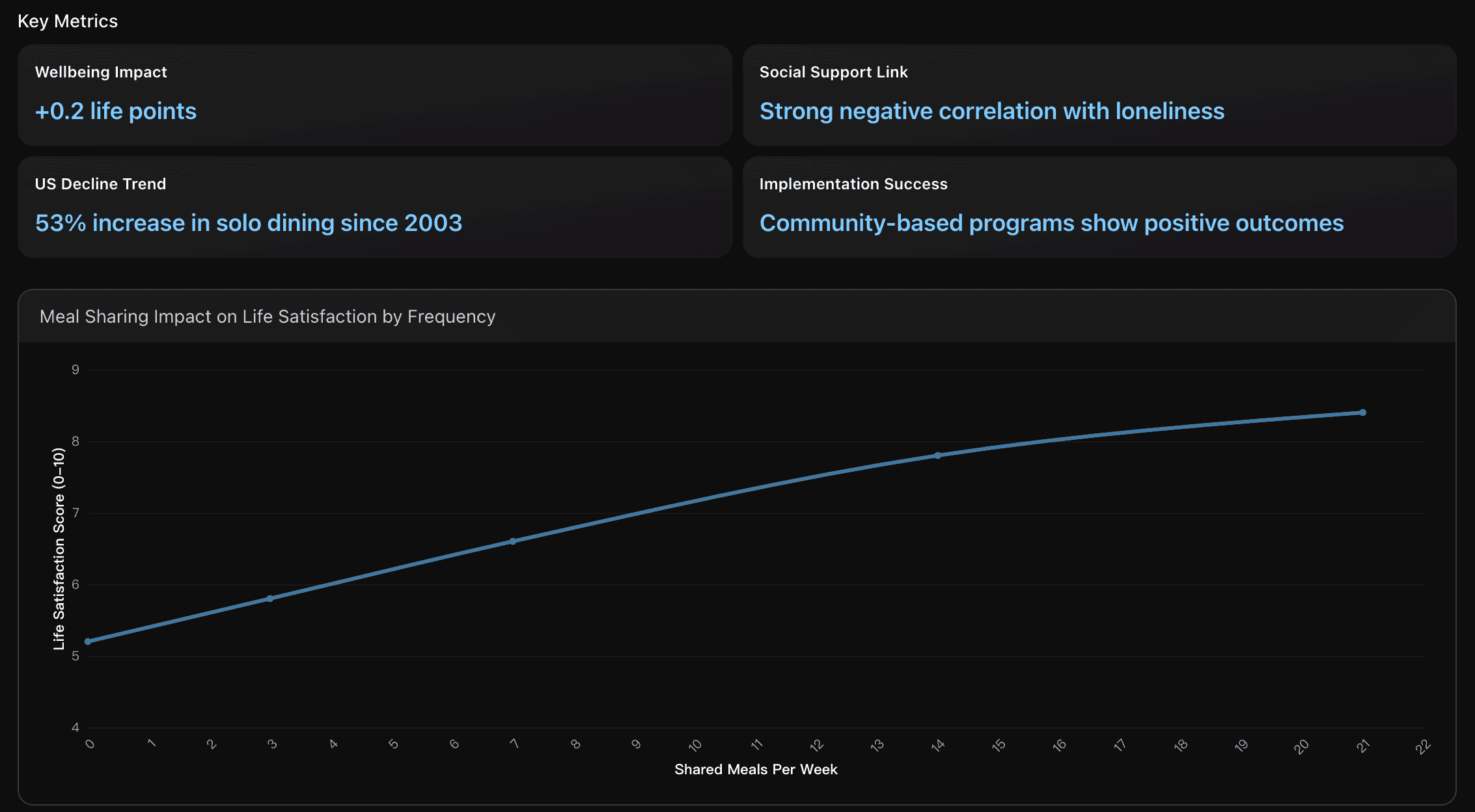
Each additional shared meal per week correlates with a 0.2-point increase in life satisfaction (0-10 scale), equivalent to moving 5 places higher in global happiness rankings. This impact magnitude matches the influence of income and employment changes, demonstrating meal sharing as a quantifiable wellbeing infrastructure component with measurable community outcomes.
Core Effect Size
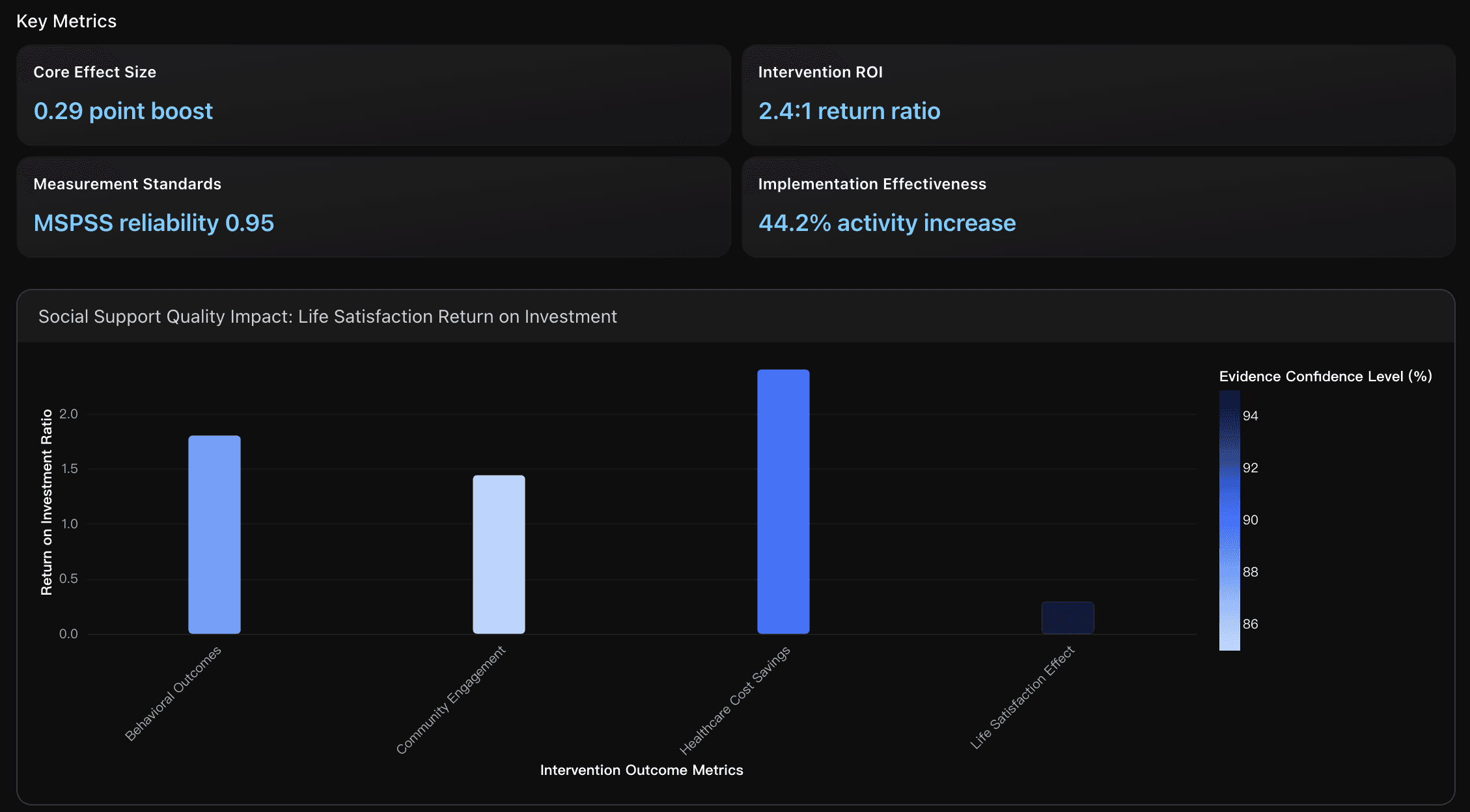
The quantitative relationship between social support quality and life satisfaction shows a 0.29-point increase in life satisfaction for every 1-point improvement in perceived social support, validated across 22 countries and 147,678 respondents in the World Happiness Report 2025. This effect size demonstrates that social support quality interventions have measurable, consistent impacts across diverse cultural contexts, making it a reliable metric for program evaluation and resource allocation decisions.
Actionable Insights
Implement a municipal-based social infrastructure framework modeled on Nordic institutional design. Establish inter-ministerial collaboration between health, social services, and community development departments to coordinate social connection interventions. Prioritize public sector employment dedicated to community work and social connection programming, as Nordic countries demonstrate highest OECD public employment rates correlating with top 4 global happiness rankings. Create systematic funding mechanisms for municipal-level community interventions that integrate meal sharing, social support programs, and wellbeing services within existing local government structures, ensuring scalable and sustainable social connection infrastructure implementation.
Implement community 'Meal Sharing Infrastructure' programs starting with pilot programs in 3-5 neighborhoods targeting high social isolation areas. Begin with weekly community dinners in existing social spaces (libraries, community centers, religious venues), providing financial micro-subsidies of $5-10 per participant following the Project Gather model. Track baseline loneliness scores and social support metrics before implementation, then measure monthly improvements in participant wellbeing. Scale successful models by partnering with local organizations (food banks, senior centers, youth groups) to create sustainable meal sharing networks that can achieve the documented +0.2 life satisfaction improvement while addressing the 53% increase in solo dining trends. Focus particularly on young adult programs and intergenerational meal sharing to maximize both social connection and community cohesion outcomes.
Implement standardized MSPSS measurement framework with 0.95 reliability coefficient to establish baseline social support quality in target communities, then deploy evidence-based community health worker interventions targeting the 0.29-point life satisfaction improvement per social support unit. Focus initial resources on high-impact programs demonstrating 2.4:1 ROI ratio through healthcare cost reductions, while utilizing the 44.2% median effectiveness increase as performance benchmarks. Establish quarterly measurement cycles using validated assessment tools to track progress toward improvement targets, ensuring sustainable program expansion through demonstrated fiscal returns and measurable wellbeing outcomes that justify continued investment and community stakeholder engagement.
Data Analysis
Nordic Model Social Infrastructure Framework
Analysis of Nordic countries' systematic approach to community- based social connection infrastructure, comparing Finland (#1 happiness), Denmark (#2), and Sweden (#4) with evidence from institutional inter-ministerial collaboration, publicly organized welfare systems, and community work approaches within municipal social sectors.
Meal Sharing as Social Connection Infrastructure
Quantitative analysis of meal sharing patterns as measurable social connection infrastructure across 142 countries, examining the correlation between communal dining frequency and wellbeing outcomes, with specific focus on implementation strategies for community programs.
Social Support Quality Metrics and Intervention Design
Evidence-based analysis of social support quality measurements and intervention effectiveness, examining the 0.29-point life satisfaction increase per 1-point social support improvement and community-level implementation strategies for scalable social connection programs.
Conclusion
The findings from the World Happiness Report 2025 make one truth undeniable: global happiness is no longer determined by economic growth alone. The real divide now lies within societies, driven by rising mental health struggles among young adults, widening happiness inequality, and declining social trust. Yet the data also provides direction. Countries that invest in social connection, trust-based governance, and early mental health intervention—such as the Nordic nations—demonstrate that wellbeing can be systematically improved through evidence-based policy and community infrastructure.
As we move into a new era of wellbeing analytics, traditional statistics alone are no longer enough. We need tools that can extract insight from complex datasets, connect human and social metrics, and generate actionable strategies. That is exactly what Powerdrill Bloom is built for.
If you want to:
Analyze global wellbeing at scale
Monitor demographic risk signals
Design data-backed policy or intervention strategies
Turn raw datasets into insight-rich narratives instantly
Then it's time to discover Powerdrill Bloom—the AI engine behind this analysis.
Start transforming your data into meaningful decisions.
Try Powerdrill Bloom today and uncover insights that matter.




